28. Februar 2025
Sustainable Funding – Principles, Concepts and Instruments
Sustainable management, and therefore sustainable funding, has become increasingly important in recent years. This raises the question of what approaches exist, what the basic concepts are and what instruments can be used to implement sustainable funding. Sustainable finance describes the integration of environmental, social and governance (ESG) aspects into financial decisions. It is based on international goals such as the United Nations 2030 Agenda and the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Important topics include climate protection, social justice and responsible corporate governance.

Prof. Dr. Thomas K. Birrer
Jean-Dominique Bütikofer, CFA
Ante Busic, PhD
Ralph Caluori, CFA
Nadine Woolley
In this respect, ESG data and ESG ratings have important functions. ESG data, which is used for evaluation, mainly comes from company reports. However, their qualitative nature makes standardization and comparability difficult. ESG ratings assess companies according to their sustainability performance and help market participants to make informed decisions. However, the methodologies used by rating agencies differ significantly, which can lead to divergent results. This needs to be taken into account.
Furthermore, the variety of instruments associated with sustainability aspects is extensive and it is possible to pursue different objectives. The following illustration provides an overview of available sustainable financing instruments, which are explained in a detailed study by the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts with many practical examples.
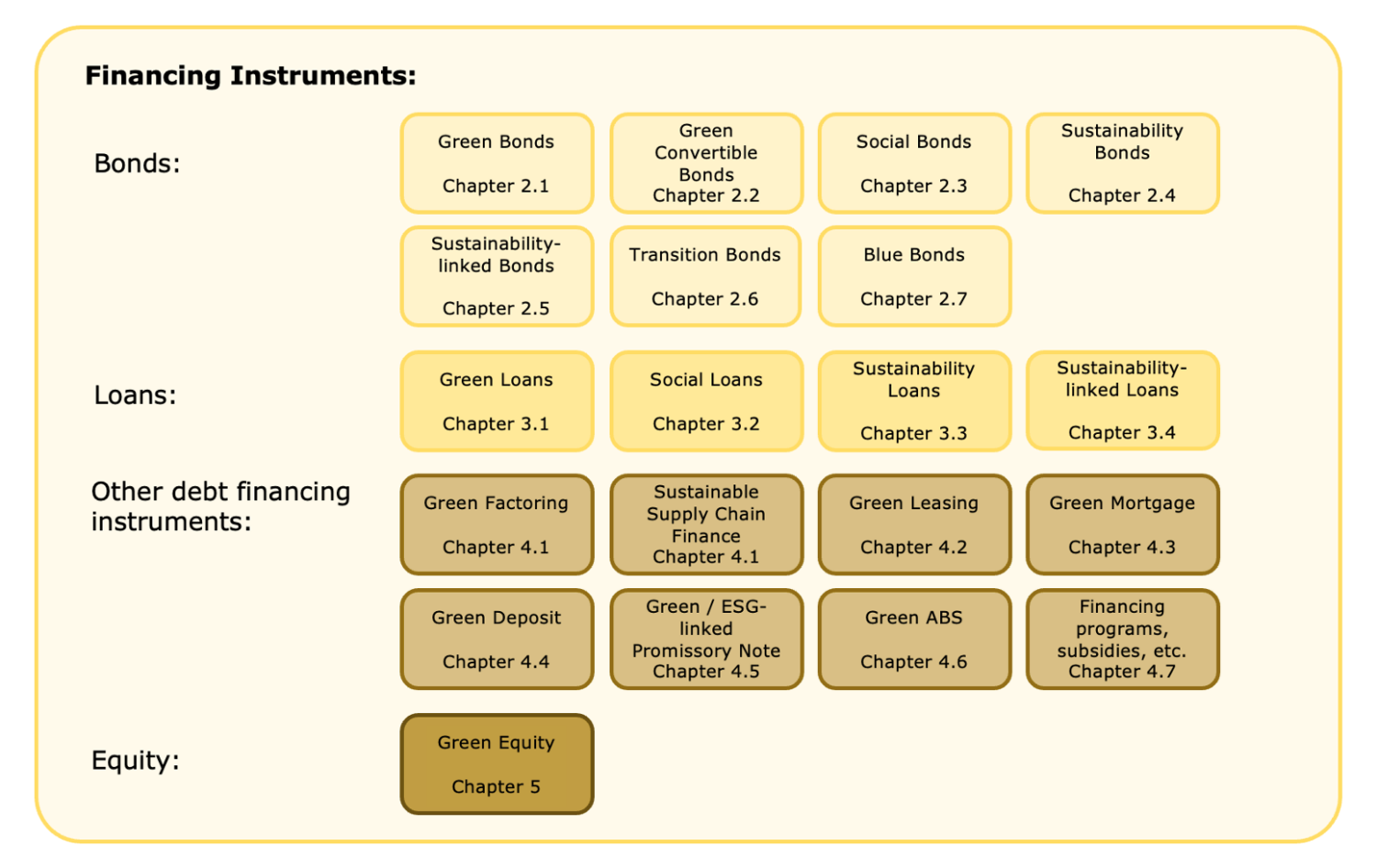
Sustainable bonds are now well known on the market. These include green bonds, which promote environmentally related projects such as the use of renewable energies, social bonds, which support social initiatives such as the construction of affordable housing, and sustainability bonds, which can combine both areas. Sustainability-linked bonds are another funding option. Here, the proceeds can be used flexibly, but are linked to the achievement of specific sustainability targets (key performance indicators, KPIs). Issuers benefit from favorable conditions if they achieve ambitious sustainability targets. Sustainable loans, including green loans and social loans as well as instruments such as green leasing, green ABS, green mortgages and ESG-linked promissory bills also contribute to financing a more sustainable economy.
Nevertheless, these instruments also entail challenges and risks that must not be ignored. Greenwashing, where companies exaggerate or misrepresent their sustainability efforts, remains a key problem. There is also the difficulty of comparing different ESG ratings with one another, as they are based on different methodologies. There is also the question of whether sustainable funding instruments actually lead to lower financing costs, which is referred to as «Greenium».
different actors need to work together. Companies, investors, regulators, NGOs and multilateral development banks play a key role in the further development of sustainable financing models. In Europe in particular, initiatives such as the Green Deal are providing important momentum.
Sustainable finance is constantly evolving. Regulatory measures such as the EU taxonomy and stricter disclosure requirements are accelerating this change, while the standardization of ESG data is becoming increasingly important. It improves transparency and comparability and thus creates a more reliable basis for sustainable investments. Innovative technologies, particularly in the area of ESG data analysis, are also becoming increasingly important and facilitate the implementation of sustainable strategies.
Detailed explanations can be found in the publication «Sustainable Funding – Principles, Concepts and Instruments», which can be downloaded for free via the following link:
Sustainable Funding – Principles, Concepts and Instruments
Nachhaltig Finanzieren – Grundlagen, Konzepte und Instrumente



Kommentare
0 Kommentare
Danke für Ihren Kommentar, wir prüfen dies gerne.